Benefits of a Dynamic Warm-up for Running
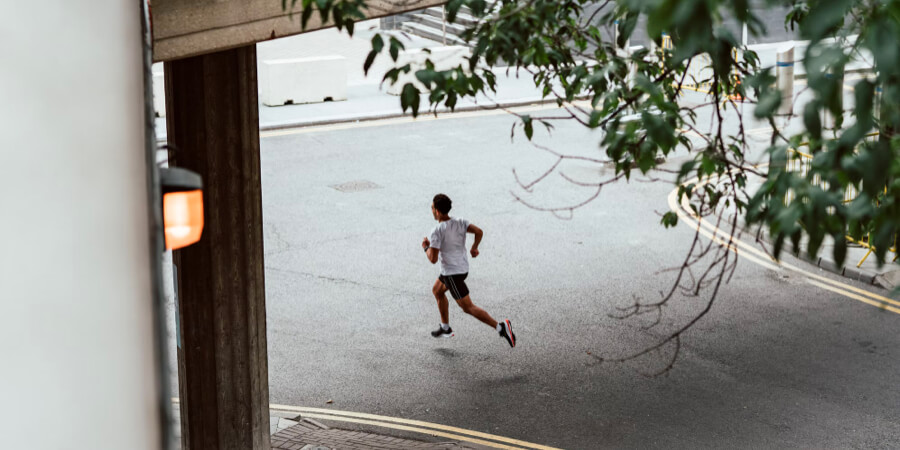
Given its simplicity and accessibility, running is an extremely popular method of exercise—all you need are a pair of running shoes, some appropriate clothing, a route to follow or access to a treadmill and you can start exercising. Want to maintain a healthy bodyweight? Running can do that. Want to improve your health or reduce stress? Running can do that. Want to test your fitness level or need some additional motivation to exercise? Register for a running race or event and you’re set.
Of course, while running is easy, accessible and beneficial, you have to know how to do it properly so you can enjoy it for years. One of the ways you can help prepare your body to perform its best once you start running is to first perform a dynamic warm-up, which offers the following six benefits:
- For many runners, a warm-up may consist of only a few stretches or some slow jogging before starting to move at a steady running pace. While this is better than nothing, it does not adequately prepare muscles for the forces experienced during a run. If you run regularly or are returning to running after taking some time off, avoid the risk of an injury and make your workouts as effective as possible with a dynamic warm-up.
- Cold temperatures require a car’s engine to idle for a few minutes to allow it to warm up before driving. Warming up a car is a fitting analogy for the benefits of a dynamic warm-up; allowing a car’s engine to run for a few minutes ensures that oil is circulated through the engine to lubricate the pistons responsible for generating the power that makes the car go. Muscle, fascia and elastic connective tissues are more elastic at higher temperatures, which allows easier, unrestricted motion of the joints used in exercise. Taking the time to perform a complete dynamic warm-up, starting with slow movements before progressing to rapid, explosive exercises, allows blood to circulate to the working muscles. This also activates the central nervous system (CNS) so it functions more efficiently to control the muscles involved in running.
- There are two general types of muscle fibers in your body: slow twitch and fast twitch. Slow-twitch fibers use oxygen to metabolize free fatty acids into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the chemical used for energy, via a process called lipolysis. Slow-twitch fibers are mostly involved with endurance activities such as running for distance. Conversely, fast-twitch fibers use carbohydrates (called glycogen once it is stored in muscle cells), either with or without oxygen, to produce ATP. Because they can generate more force than slow-twitch fibers, fast-twitch fibers are used when muscles need to produce greater amounts of force. Glycolysis, which is the process of metabolizing glycogen to ATP, takes less time than fatty acid oxidation; for this reason, it is the primary source of energy when running at a moderate-to-fast pace. The different movements of a dynamic warm-up helps facilitate glycolysis so that you can produce energy efficiently for your run.
- Several hormones, including cortisol, epinephrine and norepinephrine (commonly called adrenaline because they are produced in the adrenal glands), are used to help metabolize fats and carbohydrates to ATP. The gradually increasing intensity of a dynamic warm-up allows the adrenal complex to produce these hormones so that you have the energy to fuel your run.
- Reciprocal inhibition refers to the physiological action that occurs when the shortening or contracting of one muscle sends a signal to the muscle on the other side of a joint to lengthen. The controlled contractions of a dynamic warm-up apply reciprocal inhibition to allow muscles to lengthen and joints to lubricate to properly prepare for activity. In addition, joint capsules and ligament endings contain numerous sensory receptors that measure and identify pressure, movement and the rate of movement of their respective joints. Slow, controlled movements through a complete range of motion allows the nervous system to learn how to regulate the degrees of freedom, or amount of movement, allowed in each individual joint.
- A byproduct of glycolysis is carbon dioxide, which causes your rate of breathing to increase because the lungs are trying to expire carbon dioxide while drawing in more oxygen to use for energy production. In addition, glycogen stored in muscle cells attaches to water. As glycogen is metabolized to ATP, it releases that water in the cells. Low-intensity body-weight exercises use free fatty acids for fuel; as the exercises of a dynamic warm-up become more intense, the working muscles gradually start using glycolysis to produce ATP. This causes your breathing to speed up and sweat to start appearing, which is a signal that your muscles are ready to go, the warm-up is over and it’s time to start running!
Whether you’re a longtime runner looking for a more effective way to train or you’re a beginning runner, the following dynamic warm-up will help make sure that every step you take counts. Note: These exercises are also very effective for an active recovery workout the day after a really hard training session, when your muscles are still sore and you want to move but you don’t want to overwork your body. In addition, they can also be used for a stand-alone mobility workout on those days when you might be dragging a little bit and want to work out but don’t want to push yourself too hard.
Via: www.acefitness.org